In general, we copy/upload IOS image files to either flash or bootflash from a TFTP server. In case of timeouts or network delays with the TFTP server, we could use either USB or Memory Slots in order to copy image files to a network device. Once you are done copying the image to flash/bootflash, we can simply configure the network device itself as a TFTP server and can be used to copy image files across other devices.
NOTE: Please make sure all the devices are in the same subnet
In our example, we have used 2 Routers. Router 01 is preloaded with the Image files and will be configured as the TFTP server. Router 02 will be the TFTP client.
Step 01: Make sure, the image file is already copied to the file location (flash or bootflash)
# show bootflash:
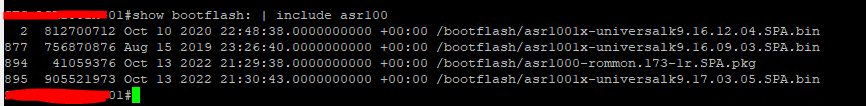
Step 02: Configure the Router as a TFTP server. And then assign the relevant image file
(config)# tftp-server bootflash:/“imagename”
![]()
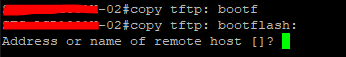
Step 03: Log into Router 02 and copy the Image file from the TFTP server (Router 01)
#copy tftp bootflash:
[source: Cisco KB]

