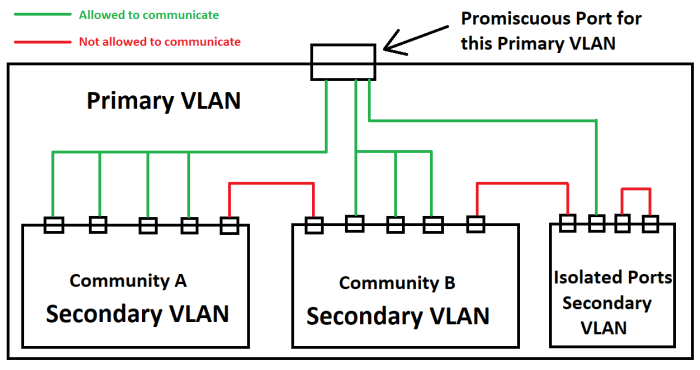
VLAN provides network isolation and layer 2. Typical VLAN would have a single subnet and all the devices within the VLAN can communicate with each other. But what if you want to put multiple devices within a subnet and do not wish to communicate with each other ? The answer would be the use of Private VLANs (PVLANs).
How it works
PVLANs are actually a set of VLANs. There is a Primary VLAN and one or more Secondary VLANs.
Primary VLAN – Same as a typical VLAN and the networks are promiscuous, as they will always communicate with each other
Secondary VLAN – These networks are associated with the Primary VLAN and they keep seperated with each other
In Secondary VLANs, there are two types of Networks
- Community VLAN – In a community VLAN, the devices will communicate with each other. But the Inter community VLAN does not take place. [ex: Community A and Community B VLANs will have no communication]
- Isolated VLAN – In an Isolated VLAN, the devices will not communicate with each other. They also have no Inter commuication with Community VLANs.
All the devices can connect to the Primary VLAN. So this allows the devices to share Internet connectivity. Basically, this will act as the default gateway.
Ports in the Primary VLAN are known as the Promiscuous Ports (P-Ports). Layer 3 switches are placed here and can have SVI (Switch Virtual Interface) configured in the Primary VLAN.
Ports in the Secondary VLANs are known as the Host Ports , as the name suggests these ports are being used to connect the end points (devices).
The below Diagram provides a good explanation