DATA backup is to make copies of particular data in order to use those copies for restoring the information if a failure occurs (a data loss event due to deletion, corruption, theft, viruses etc.).
there are four common backup types implemented and generally used in most of these programs: full backup, differential backup, incremental backup and mirror backup.
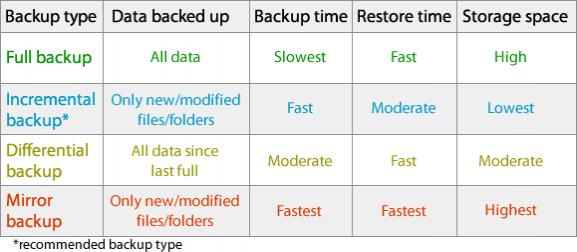
- Full backup
Full back up is the starting point for all other types of backup and contains all the data in the folders and files that are selected to be backed up.
- Differential backup
Differential backup contains all files that have changed since the last FULL backup. The advantage of a differential backup is that it shortens restore time compared to a full back up or an incremental backup.
- Incremental backup
Incremental backup stores all files that have changed since the last FULL, DIFFERENTIAL OR INCREMENTAL backup. The advantage of an incremental backup is that it takes the least time to complete.
- Mirror backup
Mirror backup is identical to a full backup, with the exception that the files are not compressed in zip files and they cannot be protected with a password. A mirror backup is most frequently used to create an exact copy of the source data.
- Smart backup
Smart backup is a backup type which combines the full, differential and incremental backup types with cleanup operations in order to efficiently manage the backups according with the backup settings and the free disk space in destination. The Smart backup type starts with a full backup.