Will focus on VMware Horizon Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) offering that is specifically designed for VMware Service Provider Partners (VSPP).
Horizon DaaS allows Service Providers to:
- Provide a single management console for provisioning and delivering virtual desktops and applications from the service provider service center
- Host multi-tenants, providing dedicated compute resources across dedicated or shared VMware vSphere clusters
- Allows tenants to bring in their own network services (Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, File Servers, etc.) to provide the same level of security and control as if the workloads were running on-premises
High Level DaaS Architecture
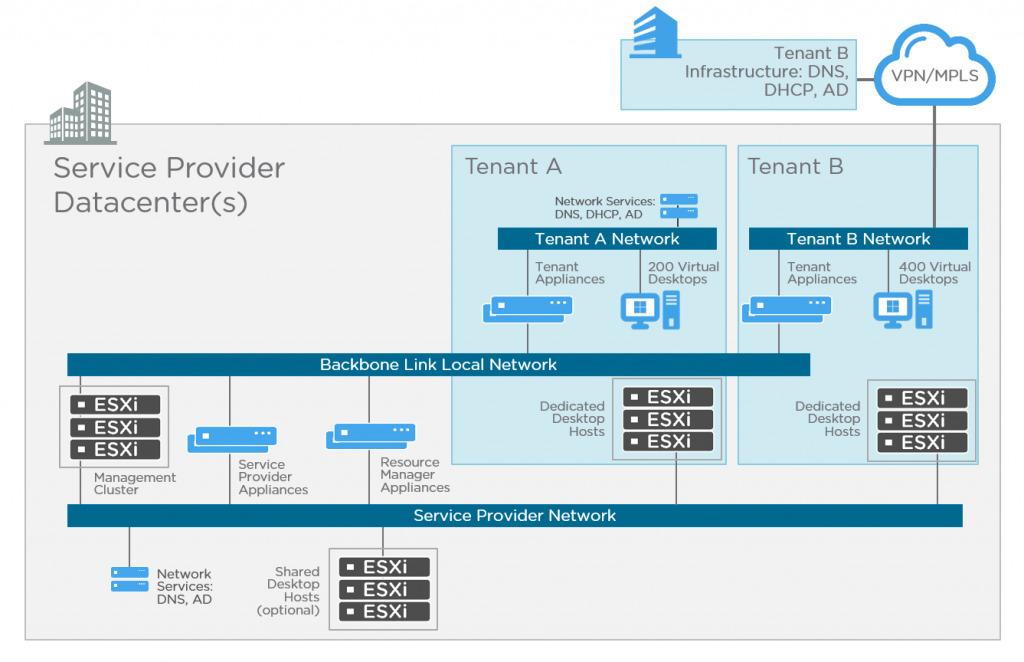
Components of VMware Horizon DaaS
Horizon Version Manager appliance – HVM Provides orchestration and automation for Horizon DaaS components. The HVM holds the appliance template, and runtime scripts, which allow for the automatic creation of the Service Provider appliances and the Resource Manager appliances. This is a Linux virtual appliance that is deployed from an OVA file in vCenter Server.
Horizon Air Link appliance – Once the HVM appliance is deployed and the template and scripts copied to the machine, the next stage to deploy the HAL appliance from the HVM admin portal. The HAL is responsible for sending API operations to the vCenter Server to create the appliances.
Service Provider appliances – This is deployed as a pair for high availability. The SP provides the Service Provider administrators access to a web-based portal (Service Center) where they can manage the Horizon DaaS environment. This is the main console from where tenants are deployed, which resource cluster they use, as well as creating desktop collections, which are essentially capacity models for virtual desktops.
Resource Manager appliances – Like the SPs, this is deployed by the HAL in a pair. The role of the RM is to provide access and show the hardware resources available from the vCenter Server(s) that is configured for Horizon DaaS. The RM allows the Service Provider administrators to configure the compute resources for the tenants by allocating resources.
Tenant appliances – The tenant appliances (pair) TA are created from the Service Center portal. You configure the settings for the tenant, such as quotas for user licensing and desktop capacity. Per tenant, a pair is being created.
Unified Access Gateway – This is a hardened Linux appliance that is deployed within the DMZ network to provide secure incoming traffic from external environments. External Horizon Clients make a connection to the UAG and do not see the backend environment, it is the UAG that communicates with the backend Horizon environment. The UAG supports multi-factor authentication to provide further security when accessing virtual desktops and applications from the Internet. The new UAGs will have the capability of SSL offloading as seen on ADC Application Delivery Controllers.
Below is the list of official documentation provided by the Vendor.
- Horizon DaaS 9.1.x Installation and Upgrade
- Horizon DaaS 9.1.x Service Provider Administration
- Horizon DaaS 9.1.x Tenant Administration
[source: vmware.com]