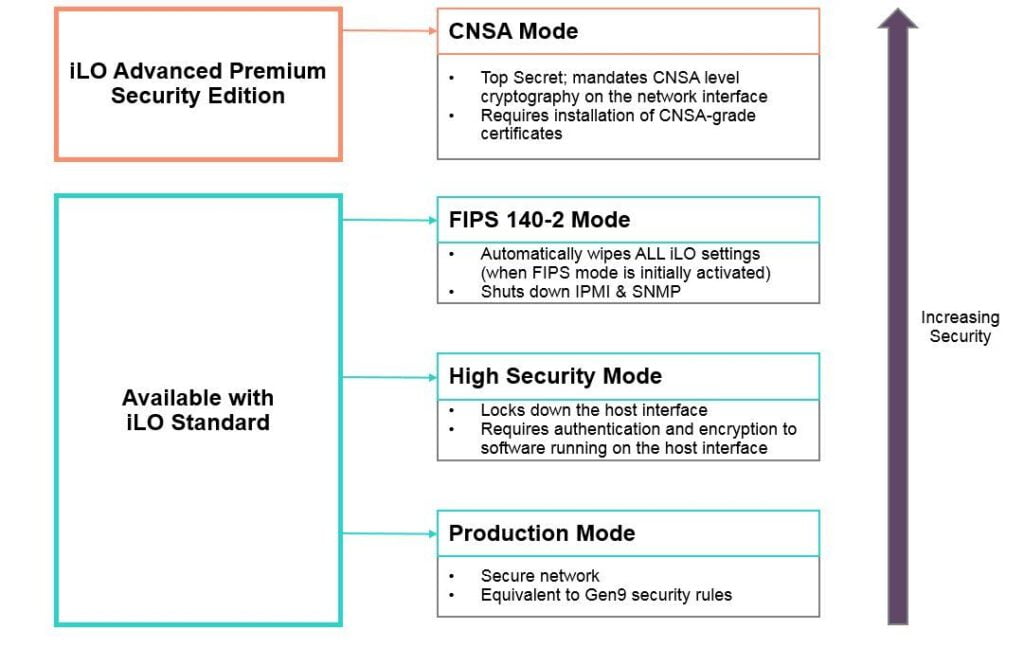
As IT professionals we are suposed to work on server systems. Also there are instances where we need to harden the server hardware infrastrcture. With HPE iLO 5 standard edition, included with every ProLiant Gen10 Server, customers get the ability to configure their servers in one of three security modes. The default is the “Production Mode”
Production Mode, High Security Mode, and FIPS Mode. With the iLO Advanced Premium Security Edition license, customers who need the highest-level encryption capabilities have a fourth mode available to them: CNSA Mode
 Lets deep dive into the FIPS modes that most of the vendors support.
Lets deep dive into the FIPS modes that most of the vendors support.
Production Mode
When set to this security mode, iLO uses the factory default encryption settings. The system maintenance switch setting to bypass iLO security (sometimes called the iLO Security Override switch) disables the password requirement for logging in to iLO.
High Security Mode
This locks down the host interface by requiring authentication from the host OS side. High security mode enforces stricter security policies such as requiring valid iLO 5 credentials to use RBSU or other host-based utilities.
FIPS Mode
FIPS Mode not only implements validated encryption ciphers (as High Security Mode does) but also closes down insecure interfaces that do not meet the government standard. Because interfaces like IPMI and SNMP v1 are shut off, potential attack surfaces are reduced. When entering FIPS mode, all the iLO 5 settings are reinitialized to operate as a FIPS validated environment.
CNSA Mode
CNSA is a suite of cryptographic algorithms approved for use by the US National Security Agency for protecting secret and top secret information with the U.S. government, and is the highest-level cryptographic algorithm available for commercial systems.
[source: HPE]